AJAX
AJAX = Asynchronous JavaScript And XML.
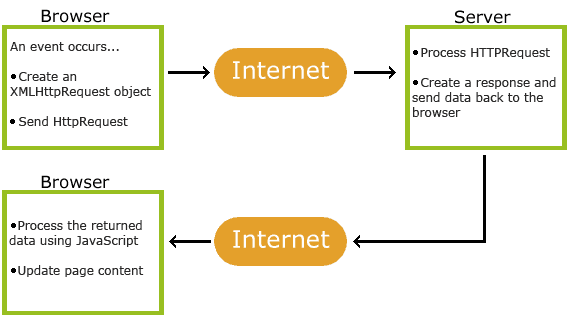
- Nešto se dogodilo na stranici (stranica je učitana, kliknuto dugme)
- JavaScript pravi XMLHttp zahtev
- XMLHttp zahtev šalje zahtev serveru
- Server obrađuje zahtev
- Server šalje odgovor web stranici
- JavaScript obrađuje odgovor
- JavaScript vrši adekvatnu radnju (ažurira stranicu i slično)
XMLHttpRequest
| XMLHttpRequest metode (methods) | |
|---|---|
| Metoda | Opis |
new XMLHttpRequest() | Kreira novi XMLHttpRequest zahtev |
XMLHttpRequest.abort() | Prekida trenutni zahtev |
XMLHttpRequest.getAllResponseHeaders() | Vraća sve informacije iz header-a |
XMLHttpRequest.getResponseHeader() | Vraća određenu informaciju iz header-a |
XMLHttpRequest.open() | Određuje svojstva zahteva |
XMLHttpRequest.send() | Šalje zahtev serveru |
XMLHttpRequest.setRequestHeader() | Definiše label i vrednost header-u |
| XMLHttpRequest svojstva (properties) | |
|---|---|
| Svojstvo | Opis |
XMLHttpRequest.onreadystatechange | Definiše funkciju koja će biti pozvana kada se readyState promeni |
XMLHttpRequest.readyState |
Sadrži status XMLHttpRequest-a: 0: zahtev nije započet 1: uspostavljena veza sa serverom 2: zahtev primljen 3: zahtev se obrađuje 4: zahtev gotov i odgovor je spreman |
XMLHttpRequest.response | Vraća ArrayBuffer, Blob, Document, JavaScript element ili DOMString |
XMLHttpRequest.responseType | Vraća tip odgovora |
XMLHttpRequest.responseURL | Vraća url odgovora |
XMLHttpRequest.responseText | Vraća odgovor kao niz |
XMLHttpRequest.responseXML | Vraća odgovor kao XML |
XMLHttpRequest.status |
Vraća status zahteva kao broj: 200 403 404 Za celu listu idi na Http Messages Reference |
XMLHttpRequest.statusText | Vraća status zahteva kao tekst:
"OK" "Forbidden" "Not Found" Za celu listu idi na Http Messages Reference |
XMLHttpRequest.timeout | Broj milisekundi nakon čega će zahtev biti prekinut |
XMLHttpRequest.upload | Is an XMLHttpRequestUpload, representing the upload process. |
XMLHttpRequestEventTarget.ontimeout | Odradi nešto nakon što je isteklo vreme i zahtev prekinut |
XMLHttpRequestEventTarget.onprogress | Odradi nešto u toku obrade zahteva |
XMLHttpRequestEventTarget.onabort | Fired when a request has been aborted, for example because the program called |
XMLHttpRequestEventTarget.onerror | Fired when the request encountered an error. Also available via the onerror property. |
XMLHttpRequestEventTarget.onload | Odradi nešto nakon što je zahtev završen |
XMLHttpRequestEventTarget.onloadstart | Fired when a request has started to load data. Also available via the onloadstart property. |
XMLHttpRequestEventTarget.onloadend | Fired when a request has completed, whether successfully (after load) or unsuccessfully (after abort or error). Also available via the onloadend property. |
| XMLHttpRequest (events) | |
|---|---|
| Event | Opis |
XMLHttpRequest.timeout | Fired when progress is terminated due to preset time expiring. Also available via the ontimeout property. |
XMLHttpRequest.progress | Fired periodically when a request receives more data. Also available via the onprogress property. |
XMLHttpRequest.abort | Fired when a request has been aborted, for example because the program called XMLHttpRequest.abort(). Also available via the onabort property. |
XMLHttpRequest.error | Fired when the request encountered an error. Also available via the onerror property. |
XMLHttpRequest.load | Fired when an XMLHttpRequest transaction completes successfully. Also available via the onload property. |
XMLHttpRequest.loadstart | Fired when a request has started to load data. Also available via the onloadstart property. |
XMLHttpRequest.loadend | Fired when a request has completed, whether successfully (after load) or unsuccessfully (after abort or error). Also available via the onloadend property. |
Metode
new XMLHttpRequest()
Sintaksa za kreiranje XMLHttpRequest zahteva:
varijabla = new XMLHttpRequest();
Varijablu mužeš da definišeš pre kreiranja zahteva ili pri samom kreiranju zahteva:
// Pre kreiranja zahteva
var xmlhttp;
xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
// Pri kreiranju zahteva
var xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
Starije verzije Internet Explorer (5/6) su koristile:
varijabla = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
Tako da možeš da napišeš:
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
var xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else {
var xmlhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
abort()
getAllResponseHeaders()
getResponseHeader()
open()
Sintaksa za određivanje svojstva XMLHttpRequest zahteva:
xmlhttp.open('metod', 'url', async, 'user', 'psw');
metod: GET ili POST
url: lokacija fajla kome se obraća
async: true (asynchronous) ili false (synchronous)
user: korisničko ime
psw: šifra
Metod
GET is simpler and faster than POST, and can be used in most cases.
However, always use POST requests when:
- A cached file is not an option (update a file or database on the server).
- Sending a large amount of data to the server (POST has no size limitations).
- Sending user input (which can contain unknown characters), POST is more robust and secure than GET.
xmlhttp.open('GET', 'ajax.php?name='+varijabla, true);// POST
xmlhttp.open('POST', 'ajax.php', true);
URL
The file can be any kind of file, like .txt and .xml, or server scripting files like .asp and .php
(which can perform actions on the server before sending the response back).
Async
Server requests should be sent asynchronously.
The async parameter of the open() method should be set to true.
By sending asynchronously, the JavaScript does not have to wait for the server response, but can instead:
- execute other scripts while waiting for server response
- deal with the response after the response is ready
Synchronous XMLHttpRequest (async = false) is not recommended because the JavaScript will stop executing until the server response is ready. If the server is busy or slow, the application will hang or stop. Synchronous XMLHttpRequest is in the process of being removed from the web standard, but this process can take many years. Modern developer tools are encouraged to warn about using synchronous requests and may throw an InvalidAccessError exception when it occurs.
send()
Sintaksa za slanje GET XMLHttpRequest zahteva:
xmlhttp.send();
Sintaksa za slanje POST XMLHttpRequest zahteva:
xmlhttp.send('niz');
Primer za slanje POST zahteva:
xmlhttp.send('name='+varijabla);
setRequestHeader()
Sintaksa za kreiranje header-a:
xmlhttp.setRequestHeader('header', 'vrednost');
header - The name of the header whose value is to be set.
vrednot - The value to set as the body of the header.
To POST data like an HTML form, add an HTTP header with setRequestHeader(). Specify the data you want to send in the send() method:
The XMLHttpRequest method setRequestHeader() sets the value of an HTTP request header. When using setRequestHeader(),
you must call it after calling open(), but before calling send(). If this method is called several times with the same header,
the values are merged into one single request header.
Each time you call setRequestHeader() after the first time you call it, the specified text is appended to the end of the existing header's content.
If no Accept header has been set using this, an Accept header with the type "*/*" is sent with the request when send() is called.
For security reasons, some headers can only be controlled by the user agent. These headers include the forbidden header names and forbidden response header names.
Primer:
xmlhttp.setRequestHeader('Content-type', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded');
Svojstva
XMLHttpRequestEventTarget
XMLHttpRequestEventTarget is the interface that describes the event handlers you can implement in an object that will handle events for an XMLHttpRequest.onprogress
XMLHttpRequest.onprogress = function (event) {event.loaded;
event.total;
};
// event.loaded the amount of data currently transfered.
// event.total the total amount of data to be transferred.
var xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest(),
method = 'GET',
url = 'https://developer.mozilla.org/';
xmlhttp.open(method, url, true);
xmlhttp.onprogress = function () {
//do something
};
xmlhttp.send();
onload
var xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();xmlhttp.open('GET', '/server', true);
xmlhttp.timeout = 2000; // time in milliseconds
xmlhttp.onload = function () {
// Request finished. Do processing here.
};
xmlhttp.ontimeout = function (e) {
// XMLHttpRequest timed out. Do something here.
};
xmlhttp.send(null);
onreadystatechange
xmlhttp.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (this.readyState == 4 && this.status == 200) {
document.getElementById("spanforresponse4").innerHTML = this.responseText;
} else {
switch (this.readyState) {
case 0: document.getElementById("spanforresponse0").innerHTML = "Unsent"; break;
case 1: document.getElementById("spanforresponse1").innerHTML = "Sent, waiting for response"; break;
case 2: document.getElementById("spanforresponse2").innerHTML = "Headers received"; break;
case 3: document.getElementById("spanforresponse3").innerHTML = "Loading"; break;
case 4:
document.getElementById("spanforresponse4").innerHTML = "Server response: "+this.status+" - "+this.statusText;
alert("Server response: "+this.status+" - "+this.statusText);
break;
}
}
};
Try:
0:
1:
2:
3:
4:
FormData
The FormData interface provides a way to easily construct a set of key/value pairs representing form fields and their values, which can then be easily sent using the XMLHttpRequest.send() method. It uses the same format a form would use if the encoding type were set to "multipart/form-data". You can also pass it directly to the URLSearchParams constructor if you want to generate query parameters in the way a form would do if it were using simple GET submission. An object implementing FormData can directly be used in a for...of structure, instead of entries(): for (var p of myFormData) is equivalent to for (var p of myFormData.entries()).
| FormData metode (methods) | |
|---|---|
| Metoda | Opis |
new FormData() | Creates a new FormData object. |
FormData.append() | Appends a new value onto an existing key inside a FormData object, or adds the key if it does not already exist. |
FormData.delete() | Deletes a key/value pair from a FormData object. |
FormData.entries() | Returns an iterator allowing to go through all key/value pairs contained in this object. |
FormData.get() | Returns the first value associated with a given key from within a FormData object. |
FormData.getAll() | Returns an array of all the values associated with a given key from within a FormData. |
FormData.has() | Returns a boolean stating whether a FormData object contains a certain key. |
FormData.keys() | Returns an iterator allowing to go through all keys of the key/value pairs contained in this object. |
FormData.set() | Sets a new value for an existing key inside a FormData object, or adds the key/value if it does not already exist. |
FormData.values() | Returns an iterator allowing to go through all values contained in this object. |
formData.append()
The append() method of the FormData interface appends a new value onto an existing key inside a FormData object, or adds the key if it does not already exist. There are two versions of this method: a two and a three parameter version:
- formData.append(name, value);
- formData.append(name, value, filename);
- name - The name of the field whose data is contained in value.
- value - The field's value. This can be a USVString or Blob (including subclasses such as File). If none of these are specified the value is converted to a string.
- filename (Optional) - The filename reported to the server (a USVString), when a Blob or File is passed as the second parameter. The default filename for Blob objects is "blob". The default filename for File objects is the file's filename.
Example:
// The following line creates an empty FormData object:
var formData = new FormData(); // Currently empty
// You can add key/value pairs to this using FormData.append:
formData.append('username', 'Chris');
formData.append('userpic', myFileInput.files[0], 'chris.jpg');
// As with regular form data, you can append multiple values with the same name.
// For example (and being compatible with PHP's naming conventions by adding [] to the name):
formData.append('userpic[]', myFileInput.files[0], 'chris1.jpg');
formData.append('userpic[]', myFileInput.files[1], 'chris2.jpg');
// This technique makes it simpler to process multi-file uploads because the resultant data structure is more conducive to looping.
// If the sent value is different than String or Blob it will be automatically converted to String:
formData.append('name', true);
formData.append('name', 74);
formData.append('name', 'John');
formData.getAll('name'); // ["true", "74", "John"]
Send by GET
HTML
Number: <input type="number" id="inputnumber"><br>
<button type="button" onclick="sendbyget()">Send</button><br>
<span id="spanforresponse"></span>
JavaScript
function sendbyget() {
var inputnumber = document.getElementById("inputnumber").value;
var xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xmlhttp.onload = function() {
document.getElementById("spanforresponse").innerHTML = this.responseText;
};
xmlhttp.open("GET", "ajax.php?number="+inputnumber, true);
xmlhttp.send();
}
PHP
$number = $_GET['number'];
echo "Your number is: " . $number;
Try:
Number:Send by POST
HTML
Number: <input type="number" id="inputnumber"><br>
<button type="button" onclick="sendbypost()">Send</button><br>
<span id="spanforresponse"></span>
JavaScript
function sendbypost() {
var inputnumber = document.getElementById("inputnumber").value;
var xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xmlhttp.onload = function() {
document.getElementById("spanforresponse").innerHTML = this.responseText;
};
xmlhttp.open("POST", "ajax.php", true);
xmlhttp.setRequestHeader("Content-type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
xmlhttp.send("number="+inputnumber);
}
PHP
$number = $_POST['number'];
echo "Your number is: " . $number;
Try:
Number:Send whole form (simple version)
HTML
<form id="formforsubmit">
Name: <input type="text" name="inputname"><br>
<input type="file" name="inputfile"><br>
<button type="button" onclick="uploadwholeform()">Send</button>
</form>
<div id="divforresponse"></div>
JavaScript
function uploadwholeform() {
var formforsubmit = document.getElementById("formforsubmit");
var divforresponse = document.getElementById("divforresponse");
var xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
var formadataforsubmit = new FormData(formforsubmit);
xmlhttp.onload = function() {
pforresponse.innerHTML = this.responseText;
}
xmlhttp.open("POST", "ajax.php", true);
xmlhttp.send(formadataforsubmit);
}
PHP
$inputname = $_POST['inputname'];
$inputfile_name = $_FILES['inputfile']['name'];
echo 'Name: ' . $inputname . '<br> File name:' . $inputfile_name;
Try:
Send file (simple version)
HTML
<input type="file" id="inputfile"><br>
<button type="button" onclick="uploadonlyfile()">Send</button>
<div id="divforresponse"></div>
JavaScript
function uploadonlyfile() {
var inputfile = document.getElementById("inputfile").files[0];
var divforresponse = document.getElementById("divforresponse");
var xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
var formdataforsubmit = new FormData();
xmlhttp.onload = function() {
divforresponse.innerHTML = this.responseText;
}
formdataforsubmit.append("inputfile", inputfile);
xmlhttp.open("POST", "ajax.php", true);
xmlhttp.send(formdataforsubmit);
}
PHP
$inputfile_name = $_FILES['inputfile']['name'];
echo 'File name: ' . $inputfile_name;
Try:
Uplad photo (complex version)
HTML
<input type="file" id="inputfile" accept=".jpg, .jpeg, .png, .gif"><br> <!-- OR accept="image/*" -->
<button type="button" onclick="uploadimage()">Send</button>
<div id="divforresponse"></div>
JavaScript
function uploadimage() {
var inputfile = document.getElementById("inputfile").files[0];
var divforresponse = document.getElementById("divforresponse");
var xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
var formdataforsubmit = new FormData();
xmlhttp.onerror = function() {
alert("An error happen while sending XMLHttpRequest.");
}
xmlhttp.timeout = 15000;
xmlhttp.ontimeout = function() {
alert("Timeout of 15 seconds passed.");
}
xmlhttp.onload = function() {
if (this.status == 200) {
divforresponse.innerHTML = this.responseText;
} else {
alert("Server response: "+this.status+" - "+this.statusText);
}
};
formdataforsubmit.append("inputfile", inputfile);
xmlhttp.open("POST", "ajax.php", true);
xmlhttp.send(formdataforsubmit);
}
PHP
$file_name = $_FILES['inputfile']['name'];
$file_size = $_FILES['inputfile']['size'];
$file_tmp = $_FILES['inputfile']['tmp_name'];
$file_type = $_FILES['inputfile']['type'];
$file_ext = strtolower(end(explode('.',$file_name)));
$check = getimagesize($file_tmp);
// Things to change:
$upload_dir = 'photos/';
$extensions = array('jpeg','jpg','png','gif');
$allowed_size = 5000000; // (in B, 1000000 is 1 MB)
if ($file_size == 0) {
echo '<p>There is no file</p>'; // Check is there any image file
} elseif ($check == false) {
echo '<p>File is not an image</p>'; // Check if image file is a actual image or fake image
} elseif (in_array($file_ext,$extensions)=== false) {
echo '<p>Not supported file format</p>'; // Check file format
} elseif ($file_size > $allowed_size) {
echo '<p>Image is too large, it must be less then ' . $allowed_size/1000000 . 'MB</p>'; // Check file size
} elseif (file_exists($upload_dir . $file_name)) {
echo '<p>Image with same name already exists</p>'; // Check is there image with same name
} else {
move_uploaded_file($file_tmp, $upload_dir . $file_name);
// Response to page:
echo '
<table>
<tr><td>File name:</td><td>' . $file_name . '</td></tr>
<tr><td>File size:</td><td>' . $file_size/1000000 . 'MB</td></tr>
<tr><td>File tmp name:</td><td>' . $file_tmp . '</td></tr>
<tr><td>File type:</td><td>' . $file_type . '</td></tr>
<tr><td>File ext:</td><td>' . $file_ext . '</td></tr>
<tr><td>Upload dir:</td><td>' . $upload_dir . '</td></tr>
</table>
<img src="' . $upload_dir . $file_name . '" alt="image" style="max-height: 100px; max-width: 200px;">
';
}
Try: